A number of ORIL compounds were tested in a series of in vitro cell growth inhibition (IC50) studies. The compounds were tested against a panel of over 40 cell lines representing a wide range of cancer indications including breast, lung, colon, ovary, prostate, melanoma and pancreas. The inhibition profiles for our lead candidate, ORIL007, in a subset of these cell lines are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. ORIL007 has been shown to have a very distinctive inhibition profile with a dramatic drop in survival for all of the cancer cells tested.
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is cellular process that occurs in physiological and pathological conditions. Apoptosis is a critical cellular function as it plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of many diseases. In some, the problem is due to too much apoptosis, such as in the case of degenerative diseases while in others, too little apoptosis is the problem. Cancer is one of the scenarios where too little apoptosis occurs, resulting in malignant cells that do not die and proliferate out of control. Apoptosis plays an important role in the treatment of cancer as it is a popular target of many treatment strategies.
The mechanism of apoptosis is complex and involves many pathways. We have demonstrated that ORIL007 induces apoptosis of cancer cells by a number of experimental approaches including Annexin V staining (Figure 2).
Figure 2. ORIL007 induces apoptosis of cancer cells as demonstrated by Annexin V staining.
Additional experiments have helped elucidate the details of ORIL007’s mechanism of action, which involves modifications of the cellular membrane. This confidential information can be made available after signature of a confidential disclosure agreement (CDA) with ORIL.
Importantly, in addition to these highly positive results in vitro, ORIL007 has also been proven to be effective against tumours in vivo. Formulated ORIL007 was administered to mice that had been inoculated with MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells or HT-29 colon cancer cells. The response, compared with vehicle, is shown in Figures 3 and 4.
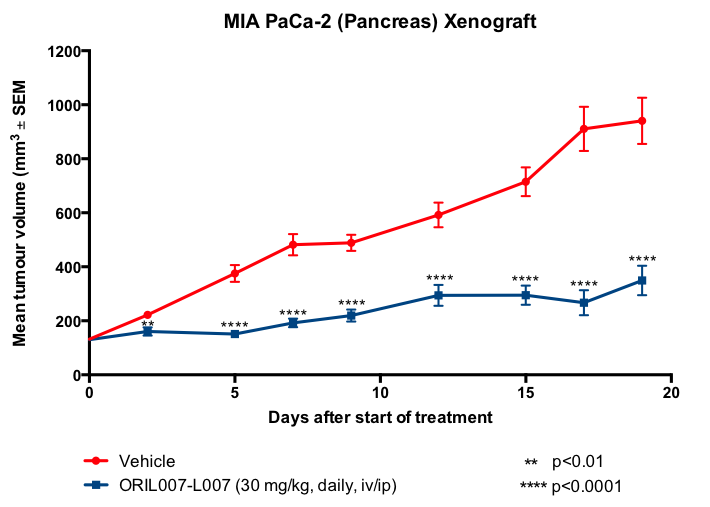
Figure 3. Parenteral treatment of mouse pancreatic cancer xenografts with ORIL007.
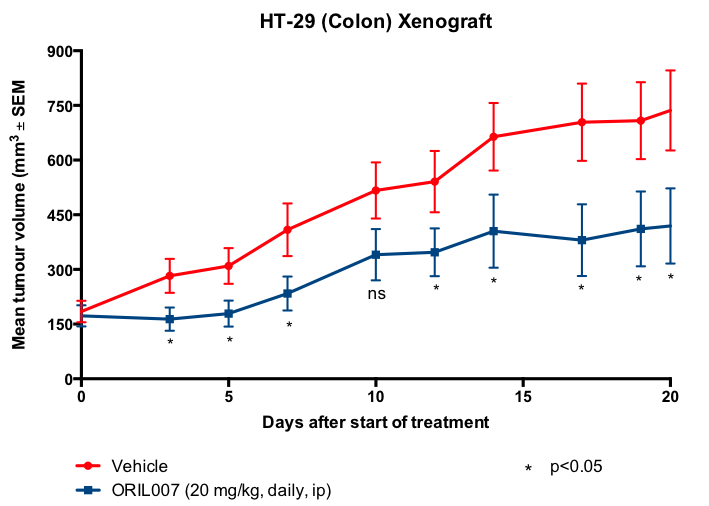
Figure 4. Parenteral treatment of mouse colon cancer xenografts with ORIL007.
In combination therapy
Increasingly, combination therapy is the preferred choice in the treatment of cancer. The following graphs illustrate the ability of ORIL compounds to act synergistically in combination with chemotherapeutic agents in several important cancer cell lines that are otherwise difficult to treat with a monotherapy.
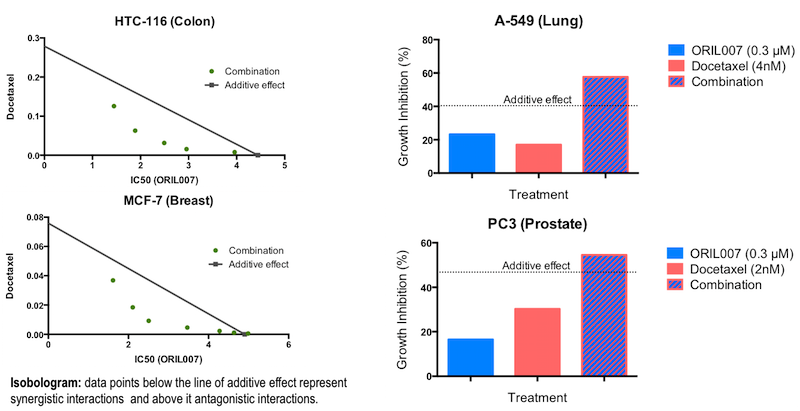
Figure 5. In vitro combination therapy with ORIL007.
In addition to the results shown in Figure 5, positive combination outcomes have also been demonstrated with other cancer agents in an ongoing program focused on optimising combination therapies using ORIL007 as one of the components.
Next generation of Compounds
Looking forward into the next generation, ORIL has designed and synthesized novel molecules which have improved pharmaceutics (and therapeutic) properties. Initial results shown below are promising in that (for example), ORIL019 has an increased in vitro potency in 5 cancer types.
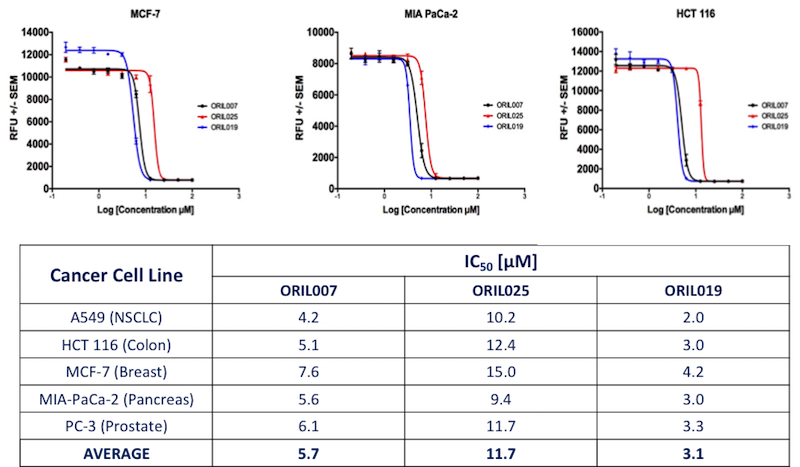
Figure 6. In vitro efficacy of ORIL019, ORIL025 and ORIL007.
Immuno-oncology
Saponins have a history of use as immuno-modulators for immunotherapies. Saponin based adjuvants have the ability to modulate the cell-mediated immune system as well as to enhance antibody production and have the advantage that only a low dose is needed for adjuvant activity. However, their use in the clinic has been limited by their poor water-solubility (making them difficult to formulate) and their toxicity. Saponins are surface active agents and can cause haemolysis of red blood cells.
ORIL saponins kill cancer cells by apoptosis (not necrosis) which is connected to slight perturbations within the plasma membrane, triggering apoptosis and potentially causing the dying cells to be attractive to phagocytic cells.
ORIL019 shows reduced lysis of human blood cells, a favourable indicator of safety, compared to the parent compound ORIL007. By comparison the commercial Quillaja derived saponin adjuvant Quil A has a HD50 of around 7 µg/mL activity while ORIL019 has an HD50 of >140 µg/mL. The company considers ORIL compounds have potential application in immuno-oncology and/or as vaccine adjuvants due to their immuno-potentiation effects.
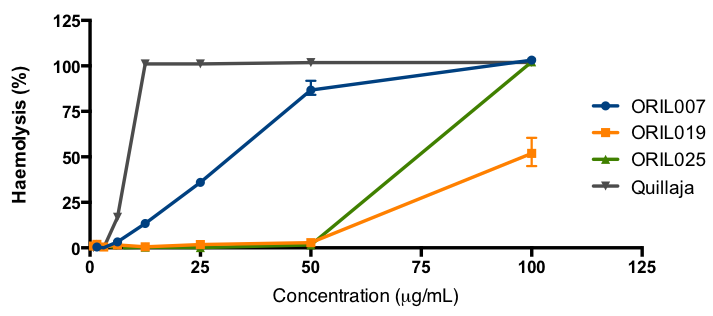
Figure 7. In vitro haemolytic activity of various ORIL compounds, compared to the saponin derived from Quillaja.
Diseases where angiogenesis is a therapeutic target
Angiogenesis is the generation of new blood vessels from pre-existing ones. It is well documented that abnormal angiogenesis is a contributing factor in, for example, cardiac disease and pathogenesis of diabetes complications. While ORIL’s major focus is cancer therapy the company is also seeking to diversify and build its product pipeline in other related therapeutic areas in which angiogenesis plays a role. This includes inflammatory diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (a precursor of bowel cancer), and diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy, particularly for the Asia-Pacific market where bowel cancer and diabetes are major public health problems.
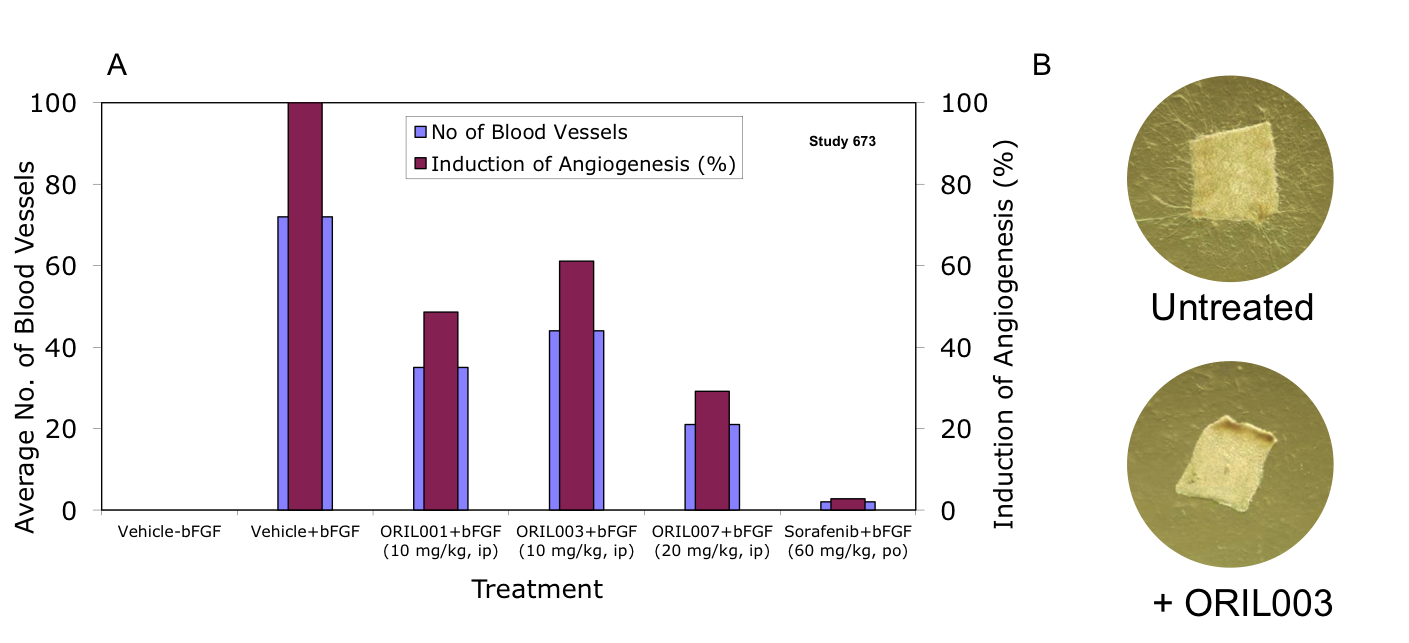
Figure 8. ORIL compounds inhibit angiogenesis as demonstrated using the AngioSponge™ (A) and the aortic explant (B) methods.
Registered Office
Oncology Research International Limited
Level 5, 45 St George Terrace,
Perth WA 6000 Australia